Understanding Digital Currencies:
The Skills You Need for a Digital World
See also: Assessing Internet Information
Digital currencies are currencies, or money systems, that are only available electronically. They can only be accessed via computers or smartphones and have no physical existence in the form of notes and coins. While the best-known example is Bitcoin, there are thousands of different digital currencies, and the technology is becoming increasingly mainstream.
Major institutions, including the Bank of England, are now exploring the creation of their own digital currencies. As these technologies become more integrated into our lives, it is essential to develop the skills to understand how they work, their advantages, and their potential risks. This is not about becoming a financial trader; it is about developing your digital literacy for an increasingly digital world.
This page will explain the basics of digital currencies and, more importantly, explore the critical thinking and analytical skills you need to evaluate these and other emerging technologies with confidence.
Types of Digital Currency
There are three main types of digital currency that you are likely to encounter.
-
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies use cryptography—a method of protecting information through complex codes—to secure and verify transactions. This means that the currencies themselves are created and managed using sophisticated computer code. For example, Bitcoin, the best-known cryptocurrency, is 'mined' by powerful computers solving complex mathematical puzzles.
Each transaction is recorded on a digital ledger called a blockchain. This ledger is not held in a central location, but is distributed across a network of computers around the world. Each user on the network holds a copy of the ledger, meaning that records are transparent and cannot be easily falsified. Because they are not controlled by central banks or governments, cryptocurrencies are described as decentralised. Indeed, many were created precisely to avoid this kind of central control.
-
Virtual Currencies
Virtual currencies are unregulated digital currencies that are typically created and controlled by their developers or an algorithm following a clear set of rules. These types of currencies are interesting because they extend the concept of currency beyond a simple 'buy and sell' transaction. Instead, they are a way of transferring value within a specific digital environment.
For example, a token in a video game may give you an extra life or a special power, but it does not have a direct cash value outside of that game. You could also argue that systems like transport cards (such as London’s Oyster card) are a form of virtual currency, as they allow users to hold and spend value for a specific purpose—in this case, travel.
-
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Central Bank Digital Currencies are regulated digital currencies that are issued and backed by a country's central bank. They can replace or supplement standard physical currency. The central banks of several countries, including Sweden and the UK, have announced that they are considering issuing a CBDC. Unlike most cryptocurrencies, these digital currencies are completely centralised.
Because they are backed by a central bank, CBDCs are likely to be much less volatile than cryptocurrencies. Investors are likely to have the same faith in them as they do in the country's physical currency, although their value can still be affected by government actions and economic policy.
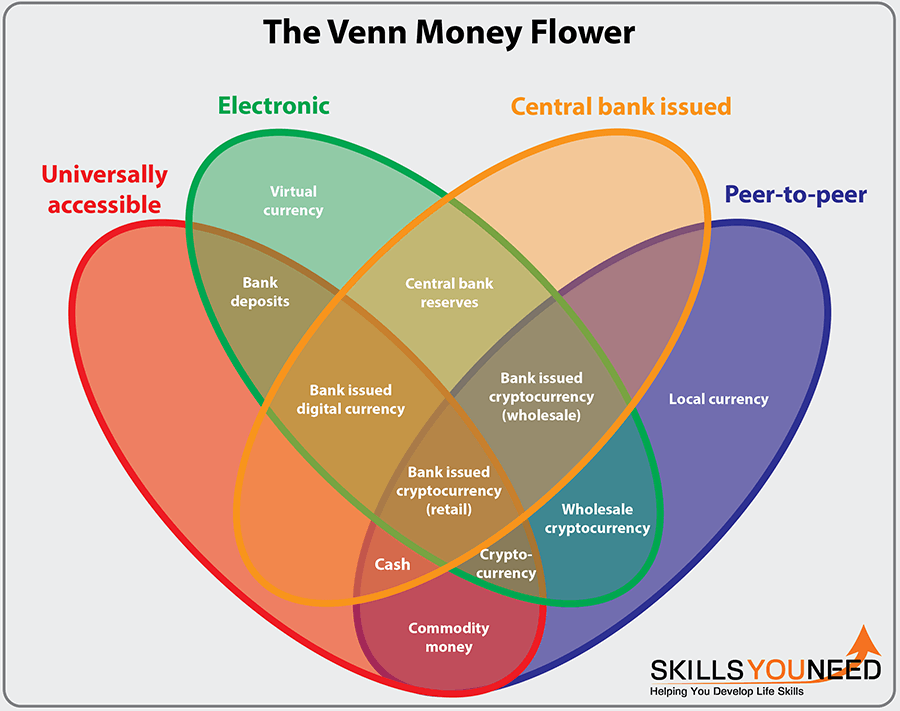
Adapted from The Bank for International Settlements
Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Currencies
Digital currencies have a number of potential advantages, but also some significant drawbacks.
Advantages of Digital Currencies
Fast transaction times. Because transactions often do not need a traditional intermediary like a bank, they can be much faster than transfers of physical money, especially across borders.
Transparency of process. The electronic nature of the transfer provides a clear record of every transaction. Whether via a bank’s internal systems or a public blockchain, the transactions are visible and auditable.
Reduced costs of transfer. By making transactions more direct, digital currencies can reduce the number of intermediaries involved, which can make transactions cheaper.
No physical manufacturing requirements. Unlike physical money, you do not need to mint coins or print notes, or worry about them being damaged in circulation.
Disadvantages of Digital Currencies
-
They still require significant infrastructure. You may not need bank vaults, but digital currencies still need a vast and complex infrastructure of computer hardware and networks to be stored and processed. This is not without cost, especially in terms of energy.
The Environmental Cost of Some Cryptocurrencies
You may think that digital currencies are cost-free to produce, but this is not true, especially for some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Bitcoin's 'dirty secret' is that its "proof-of-work" mining process takes an enormous amount of computer power, because it can only be done by solving increasingly complex computer problems. This means that it uses a huge amount of energy. Indeed, some estimates suggest that the Bitcoin network uses as much energy each year as a small country.
While some argue that much of this energy is from renewable sources, the high energy consumption remains a serious environmental concern. It is, therefore, possible that some cryptocurrencies are, quite literally, costing us the earth.
Digital currencies are not always secure. Just as physical currencies are vulnerable to counterfeiters, digital currencies are vulnerable to hackers. Hackers may steal currency from digital wallets or, in some cases, attack the underlying code of a project, affecting its value. Nobody has managed to completely solve this problem yet.
Digital currencies can be very volatile. All currency values depend on investor confidence. However, it can be much harder to have confidence in a new digital currency, especially if you do not understand its purpose or technology. The history of cryptocurrencies has shown huge swings in value over very short periods.
Essential Skills for Evaluating Digital Technologies
Not all digital currencies are equal, and they carry different characteristics and risks. To navigate this complex world, you do not need to be an investor, but you do need a strong set of analytical and critical thinking skills. These are the abilities that will help you to assess any new technology you encounter.
Critical Thinking and Healthy Scepticism
The world of new technology is full of hype and strong opinions. The most important skill you can have is the ability to think critically and apply a healthy dose of scepticism to any claims you hear. When you encounter a new digital currency or any other tech trend, ask yourself some fundamental questions:
What problem does this technology actually solve? Does it have a real-world use case, or is it just a solution in search of a problem?
Who is promoting this, and what might their motivation be? Are they an objective expert or someone with a financial stake in its success?
What are the potential downsides or risks that are not being talked about?
This ability to question assumptions and look beyond the marketing is a core component of critical thinking.
Research and Information Literacy
To answer the questions above, you need strong research methods skills and a high level of information literacy. Do not rely on a single source of information, especially social media. Instead, learn to seek out and evaluate information from a variety of sources. For a new digital project, this might include:
The Project's "Whitepaper": This is a technical document that should explain what the project does, the technology behind it, and its goals. While often complex, it is a primary source of information.
Independent News and Analysis: Look for articles from reputable financial or technology journalists who have analysed the project objectively.
Community Forums and Developer Discussions: See what other developers and informed users are saying about the project. Are they excited? Sceptical? This can provide valuable insight.
The skill lies in being able to synthesise these different sources to form your own, well-rounded opinion, and to spot the difference between genuine analysis and promotional content.
A Risk Management Mindset
Finally, it is essential to approach any new technology with a risk management mindset. This is not just an investment skill; it is a life skill. It involves being able to identify potential risks and weigh them against the potential benefits. In the context of digital currencies, this means understanding the risks of volatility, the security risks of hacking and scams, and the ongoing regulatory risks from governments. By developing a clear-eyed view of the potential downsides, you can make much more informed and rational decisions about how or if you choose to engage with these new technologies.
Conclusion
The development of digital currencies is an ongoing process, and it is a fascinating and important part of our increasingly digital world. You do not need to be an expert investor or a computer scientist to understand the basics. However, you do need to be an active and critical thinker.
By developing your skills in critical thinking, research, and risk management, you can learn to evaluate these and other emerging technologies with confidence. This is not about predicting the future value of Bitcoin; it is about building the digital literacy skills you need to navigate the future with wisdom and clarity—and manage your digital legacy.
About the Author
This article was written by the SkillsYouNeed editorial team, with contributions from writers and researchers who specialise in digital literacy and emerging technologies. Our goal is to provide clear, unbiased information to help you develop the skills to understand a complex world.
